Google just got better at understanding your trickiest searches
A new machine learning algorithm is helping Google tell which words in queries matter most – and how they relate to each other.

For Google’s namesake search engine, delivering the right results is about understanding what people are asking for. And understanding that involves zeroing in on the meaningful keywords in a search query and ignoring the rest. Words like “a” and “the,” for instance, can generally be safely ignored.
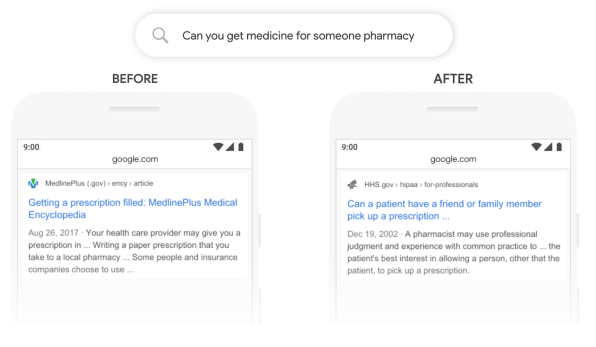
The problem is that there are lots of searches where it’s difficult for even a search engine as smart as Google to know how the words relate to each other and which ones matter. One example the company provides: If a user searches for “can you get medicine for someone pharmacy,” the “someone” is absolutely critical, since it’s shorthand for “someone other than myself.” A person would likely infer that that; a traditional search algorithm, not so much.
But now Google is rolling out an update to its English-language search engine designed to give it a deeper understanding of such subtle queries, which will let it deliver more relevant results. For the above search, results are now topped with a “featured snippet” involving the specific issue of picking up another person’s prescription. (Previously, the snippet involved prescriptions but failed to address the specific gist of the query.)
I attended a press preview at Google headquarters earlier this week, where some of company’s search executives showed examples of the new algorithm’s improved results and explained the new technology that went into them. And they set the bar high for expectations; VP of search Pandu Nayak called them “the single biggest change we’ve had in the last five years and perhaps one of the biggest since the beginning of the company.”
BERT AT WORK
Under the service, the new improvements leverage a technology developed at Google called BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. We non-AI scientists don’t have to worry about what encoders, representations, and transformers are. But the gist of the idea is that BERT trains machine language algorithms by feeding them chunks of text that have some of the words removed. The algorithm’s challenge is to guess the missing words—which turns out to be a game that computers are good at playing, and an effective way to efficiently train an algorithm to understand text. From a comprehension standpoint, it helps “turn keyword-ese into language,” said Google search chief Ben Gomes.
“The more text, the better the understanding,” said Google senior VP of research Jeff Dean—and fortunately, there’s no shortage of written material out there that Google can pour into BERT. (And oh, the “Bidirectional” part of the acronym references the fact that this technique moves away from the more conventional practice of analyzing text a word at a time from left to right.)
Using supercomputers it designed itself to train machine learning models, Google is applying BERT to give its search algorithm a deeper understanding of search queries and web pages that contain relevant information. Other tech companies have embraced BERT and are using their own variants for a variety of purposes: Facebook, for instance, is using a version called RoBERTa in chatbot research. But these new Google search tweaks are an early instance of BERT coming out of the lab and improving one of the world’s most widely used services.
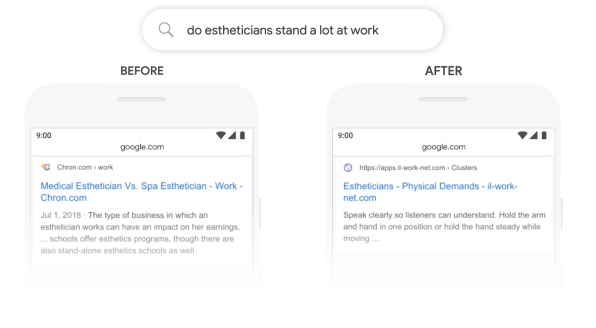
The new BERT training is only one of an array of elements that Google calls upon to choose results for any given search; the company says that it will come into play in around 1 out of 10 searches. But that 10% should include some of the ones that were most likely to stump Google in the past, such as “How old was Taylor Swift when Kanye went onstage?” and “Do estheticians stand a lot at work?”
Under the service, the new improvements leverage a technology developed at Google called BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. We non-AI scientists don’t have to worry about what encoders, representations, and transformers are. But the gist of the idea is that BERT trains machine language algorithms by feeding them chunks of text that have some of the words removed. The algorithm’s challenge is to guess the missing words—which turns out to be a game that computers are good at playing, and an effective way to efficiently train an algorithm to understand text. From a comprehension standpoint, it helps “turn keyword-ese into language,” said Google search chief Ben Gomes.
“The more text, the better the understanding,” said Google senior VP of research Jeff Dean—and fortunately, there’s no shortage of written material out there that Google can pour into BERT. (And oh, the “Bidirectional” part of the acronym references the fact that this technique moves away from the more conventional practice of analyzing text a word at a time from left to right.)
Using supercomputers it designed itself to train machine learning models, Google is applying BERT to give its search algorithm a deeper understanding of search queries and web pages that contain relevant information. Other tech companies have embraced BERT and are using their own variants for a variety of purposes: Facebook, for instance, is using a version called RoBERTa in chatbot research. But these new Google search tweaks are an early instance of BERT coming out of the lab and improving one of the world’s most widely used services.
The new BERT training is only one of an array of elements that Google calls upon to choose results for any given search; the company says that it will come into play in around 1 out of 10 searches. But that 10% should include some of the ones that were most likely to stump Google in the past, such as “How old was Taylor Swift when Kanye went onstage?” and “Do estheticians stand a lot at work?”.
In the end, BERT probably won’t have as obvious an impact on results as past Google milestones such as universal search and the knowledge graph, both of which fundamentally revised the presentation of search results in ways you couldn’t help but notice. With the addition of BERT, results still look the same; if BERT makes them better, you’ll benefit—but you’ll never know that they would have been inferior in its absence.
And even then, Nayak cheerfully acknowledges that there are instances when the BERT-infused search results are worse than the old ones. At the press event, he showed a sample: When asked “What state is south of Nebraska?” the BERT result involved the neighborhood of South Nebraska in Tampa, Florida, and was not just less relevant than its non-BERT predecessor but downright useless. But Google’s testing shows such instances are rare enough that using BERT provides a clear overall advantage, which should increase as the company tweaks the technology over time.
“BERT is not like some magic bullet that solves all problems, but it does solve a lot of problem areas,” said Nayak. “There’s still more work to do.”
By: HARRY MCCRACKEN
Source: https://www.fastcompany.com/90422132/google-just-got-better-at-understanding-your-trickiest-searches
More From Blog
October 28, 2025
Australia’s Fintech Revolution: Trends Shaping the Future of Digital Finance
Australia has emerged as one of the most dynamic fintech hubs in the Asia-Pacific region, driven by strong consumer demand for digital financial services, supportive government regulations, and the widespread adoption of innovative technologies. As the industry matures, the imperative for digital transformation has become unmistakable: fintechs and financial institutions alike are under pressure to […]

August 12, 2025
AI and Big Data in Building Smart Insurance Platforms
The insurance industry is now standing at a pivotal moment in its digital evolution. Traditional insurance models built on historical data analysis and reactive risk assessment are rapidly giving way to intelligent, predictive platforms powered by artificial intelligence and big data analytics. This transformation represents more than technological modernization; it’s a fundamental reimagining of how […]

July 23, 2025
Insurtech’s Game-Changing Trends: How AI and Digital Transformation Are Reshaping Insurance
The financial technology sector is experiencing unprecedented change, making it essential for business leaders and technology professionals to stay ahead of emerging innovations. Throughout 2025, insurance technology (insurtech) has emerged as a powerful catalyst for change, fundamentally altering how insurance providers conduct business, engage with clients, and assess risks. This technological evolution represents more than […]

April 4, 2024
Big Data Performance: Maximize Your Business Value
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly generating and collecting immense amounts of data to understand their customers more deeply. This data, often referred to as “big data,” holds immense potential for organizations to seek opportunities and overcome challenges. But accessing and analyzing big data isn’t enough to have proper strategies; organizations must pay attention to […]

April 4, 2024
How Real-Time Data Analysis Empowers Your Business
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, the ability to quickly make data-driven decisions has become a key differentiator for success. Real-time data analysis, the process of analyzing data as soon as it’s generated, has emerged as a powerful tool to empower business across industries. By leveraging real-time data analysis, organizations can gain timely and actionable insights, […]
April 4, 2024
Differences Between Data Science and Computer Science
Data Science and Computer Science are distinct fields overlapping in certain areas but have different focuses and objectives. The article below will help you clearly understand the differences and the close connection between the two fields. What is Data Science? Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that combines scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to […]

